The Central Meteorological Observatory issued another rainstorm warning to guard against urban waterlogging and do a good job in farmland drainage
China Meteorological Network News At 10: 00 on June 11, the Central Meteorological Observatory continued to issue a blue rainstorm warning. It is estimated that there will be heavy rainstorms in southern Jiangnan, central, eastern and southern South China, southeastern and western Yunnan, and Taiwan Province from 14: 00 on the 11th to 14: 00 on the 12th, including heavy rainstorms (100-150 mm) in parts of southwestern Jiangxi, central and southern Fujian, southeastern Guangxi, central and western Guangdong, and southern Taiwan Province. These local areas are accompanied by strong convective weather such as short-term thunderstorms and strong winds.
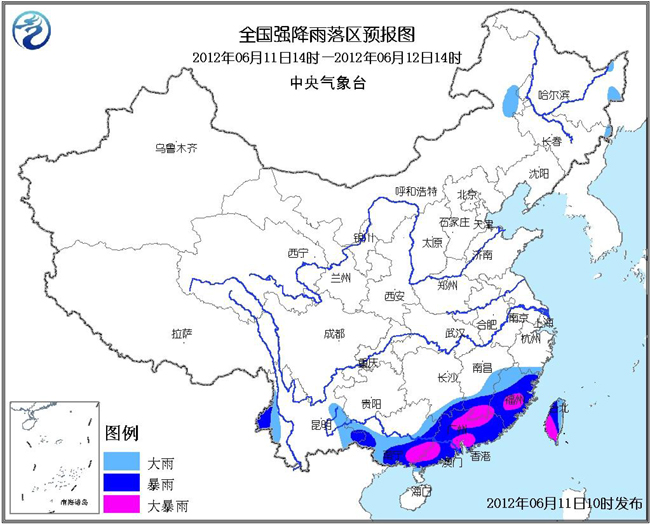
The meteorological department suggested that the government and relevant departments should do a good job in emergency prevention of rainstorm according to their duties, and all departments should strengthen information communication and emergency linkage; Do a good job in the drainage of cities and farmland, and pay attention to prevent possible disasters such as flash floods, landslides and mudslides; Cut off the outdoor power supply in dangerous areas and suspend outdoor work; The public should take measures to deal with the rainstorm and make reasonable arrangements for travel, production and life.
(Source: Editor of Central Meteorological Observatory: Li Wenqin)
[Meteorological Science Popularization]
Rainstorm and its prevention and response
Heavy rain refers to rain with high precipitation intensity, which is often formed in cumulonimbus clouds. According to meteorological regulations, rain with an hourly rainfall of more than 16 mm, or a continuous rainfall of more than 30 mm for 12 hours and a 24-hour rainfall of 50 mm or more is called "rainstorm". According to its precipitation intensity, it is divided into three grades, that is, the 24-hour precipitation is 50-99.9 mm, which is called "rainstorm", the 100-249.9 mm is called "heavy rainstorm" and the 250 mm is called "extraordinary rainstorm". However, due to the different characteristics of precipitation and topography, the standards of rainstorm and flood in different places are also different. In business practice, rainstorm can be divided into local rainstorm, regional rainstorm, large-scale rainstorm and extra-large rainstorm according to the scope of occurrence and influence.
The local rainstorm lasts only a few hours or dozens of hours, and generally affects tens to thousands of square kilometers, causing less harm. However, when the rainfall intensity is extremely high, it can also cause serious casualties and property losses.
Regional rainstorm generally lasts for 3 ~ 7 days, and the influence range can reach 100 ~ 200,000 square kilometers or more. The disaster situation is average, but sometimes it may cause serious regional rainstorm and flood disaster due to the extremely strong rainfall intensity.
Extra-large-scale rainstorm lasts the longest, and it is generally a combination of continuous rainstorms in many areas. The rainfall can last intermittently for about 1 ~ 3 months, and the rain belt can be maintained for a long time. Torrential rain is a kind of disastrous weather, which often causes floods and serious soil erosion, leading to major economic losses such as engineering accidents, dike breaches and crop flooding. Especially for some low-lying and closed terrain areas, rainwater can not be quickly vented, resulting in farmland water accumulation and soil moisture over-saturation, which will cause more disasters.
How does the city "Rain Island" avoid waterlogging?
At present, China is at the peak of urbanization, population and wealth are constantly concentrated in cities, and the area of cities is getting bigger and bigger. Urban waterlogging not only brings inconvenience to people’s travel and life, but also may cause some secondary disasters. How to carry out scientific planning and design to ensure people’s travel and property safety?
Urban "Rain Island Effect" and "Turbid Island Effect"
Urban waterlogging refers to the phenomenon of waterlogging disaster in cities due to heavy precipitation or continuous precipitation exceeding urban drainage capacity. The amount of precipitation in a city depends firstly on the atmospheric circulation and secondly on the environmental conditions of the city itself.
Modern urban waterlogging has two characteristics: first, the universality of urban waterlogging exists in many cities in China. Secondly, the incidence of waterlogging is high in some specific places in the city, such as overpasses; With the construction of modern cities, underpasses, railway bridges and highway bridges crossing the street also occur frequently. In addition, in recent years, the phenomenon that precipitation in many cities is obviously greater than that in the surrounding suburbs has become more and more prominent.
High-rise buildings in cities are compared to "reinforced concrete forests", and with the increasing density of "forests", air conditioners and automobile exhaust increase the heat, forming a hot air flow over cities. The thicker the hot air flow, the more likely it is to cause precipitation. At the same time, the concentrated buildings in the city reduce the wind speed, and the weather system such as strong rain belt stays over the city longer than the empty suburbs, and the total precipitation increases, which is called the "rain island effect". The "rain island effect" mainly appears in flood season and rainstorm, and the frequency and intensity of urban rainstorm are higher than those in surrounding areas, which is easy to form flood disasters.
The concentration of industry, the large number of vehicles and the dense population in the city lead to the turbidity of polluted gases and dust in the air much higher than that in the surrounding areas, forming the urban "turbidity island effect". The influence of urban "turbid island effect" on rainfall is as follows: dust and other turbid substances are the most needed condensation nuclei for water vapor in clouds to change into rainfall. The more condensation nuclei there are over the city, the easier it is for water vapor to condense here and cause precipitation, thus increasing rainfall.
Generally speaking, the factors affecting urban waterlogging mainly include three aspects. One is rainfall, especially heavy rainfall. When the frequency and intensity of rainstorm in cities are higher than those in surrounding areas, it is easier to form flood disasters. The second is topography. It is not easy to form stagnant water in areas with relatively high terrain, but it is easy to form waterlogging in areas with relatively low terrain, which is also the reason why a large amount of stagnant water is easy to appear in overpasses and underground passages. Third, the urban drainage system is not perfect. In some cities, there are many "debts" in the drainage network, the pipes are aging and the drainage standards are relatively low. In addition, a large number of hard pavements, such as asphalt pavement and cement pavement, have poor permeability and are easy to cause water accumulation.
How to effectively deal with the super-standard rainstorm
Unexpected events such as super-standard rainstorm will pose a great threat to urban waterlogging. Xie Yingxia, director of the Institute of Engineering Planning and Design of China Urban Planning and Design Institute, believes that combining engineering measures with non-engineering measures is an effective way to deal with the super-standard rainstorm, and it should be comprehensively considered from the aspects of economy and environment. First of all, for hard engineering measures, the standards should be appropriate and the emergency rescue system should be improved. When planning and designing, we should implement the construction contents, such as where to build reservoirs, where to divert floods, where to build pumping stations and where to build gates. Secondly, for soft non-engineering measures, it is necessary to strengthen the construction of emergency system and ensure its normal operation. In recent years, foreign countries have used ecological methods to improve the conditions of rainwater system, such as using permeable bricks to pave sidewalks, increasing permeable layers and reducing hard pavement. Storage regulation is also one of the main measures they usually take.
In addition, considering the environment, it is necessary to build an eco-city to meet the scientific development of the city. It is a good idea to beautify the city and store water and prevent waterlogging, such as increasing green space, reducing runoff, and using permeable bricks in sidewalks, squares and other areas. At the same time, planning and design methods that are economical, environmentally friendly and timely drainage are also needed to be strongly advocated.
So, how to carry out scientific planning and design to deal with urban waterlogging? Xie Yingxia said: First, we should update our concepts and pay attention to the problem of urban drainage; Second, it is necessary to introduce urban drainage planning and design standards as soon as possible, clarify the different drainage standards of different cities, and rationally arrange drainage facilities; Third, we should rationally choose urban construction land; Fourth, rational planning, scientific management, and targeted drainage planning; Fifth, we should take precautions against excessive rain, and reduce the loss of waterlogging by strengthening meteorological forecast and improving emergency management system; Sixth, we should gradually improve the construction standard of drainage system; Seventh, we must formulate good drainage measures. According to the local topography, the measures of flood interception, diversion and storage are studied; Eighth, we should pay attention to taking non-engineering measures, and it is strictly forbidden to occupy shed covers on both sides of the river, fill ditches and build land, and block the river bed. River ditches should be dredged in time to ensure smooth drainage.