Multi-picture direct hit! On the earthquake relief exercise in the plateau and alpine region
Cctv news(Reporter Liu Ruirui, reporter from Wang Xiaoying): On May 11th, the "Emergency Mission 2022" earthquake relief exercise was held in Zhangye, Gansu Province.
The exercise simulated a 7.5-magnitude earthquake in Ganzhou District, Zhangye City, Gansu Province. The epicenter was located in Xindun Village, Xindun Town, Ganzhou District, and Jiayuguan, Jinchang, Jiuquan and Wuwei felt strong earthquakes.
According to the setting, in this exercise, the "earthquake" caused houses to collapse and damage, and a series of secondary disasters occurred one after another … …
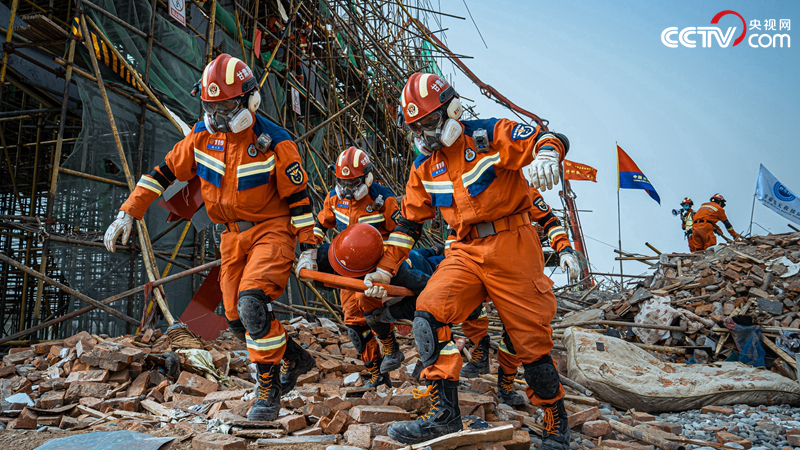

A trapped person was successfully rescued, and the fire rescue personnel transferred the personnel.
Under the majestic Qilian Mountains, on the vast Gobi Desert, fire engines lined up in turn, drones vacated and helicopters roared.
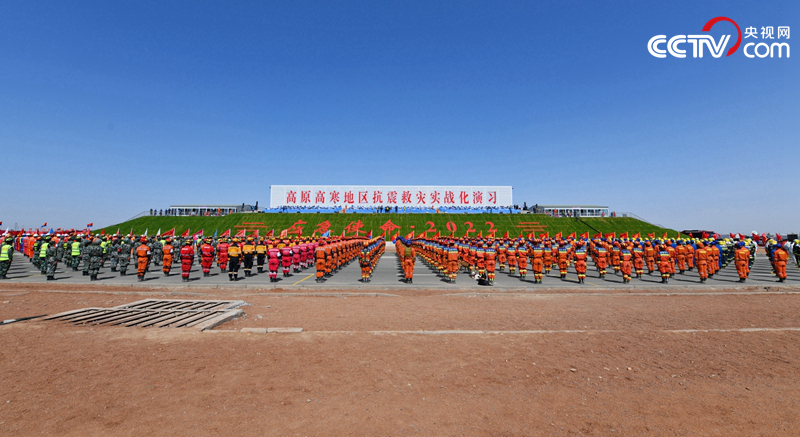

Team assembly
Number one: an earthquake of magnitude 7.5.
The exercise simulated a 7.5-magnitude earthquake in Ganzhou District, Zhangye City, Gansu Province. The epicenter was located in Xindun Village, Xindun Town, Ganzhou District, and Jiayuguan, Jinchang, Jiuquan and Wuwei felt strong earthquakes.

Rescuers made wooden supports to reinforce the collapsed building to prevent secondary collapse.
The 7.5-magnitude "earthquake" spread to many places, and a large number of houses collapsed and damaged, and a large number of people were trapped under pressure, resulting in multiple secondary disasters, including partial interruption of roads, electricity, water supply, gas and communication, landslides and collapses in mountainous areas, leakage and explosion in Ganzhou section of the west-to-east gas pipeline, overturning of trains in Europe on Lanzhou-Xinjiang line, damage to the west-to-east power transmission project, a large number of tourists trapped in scenic spots, and some villages formed "islands" & …
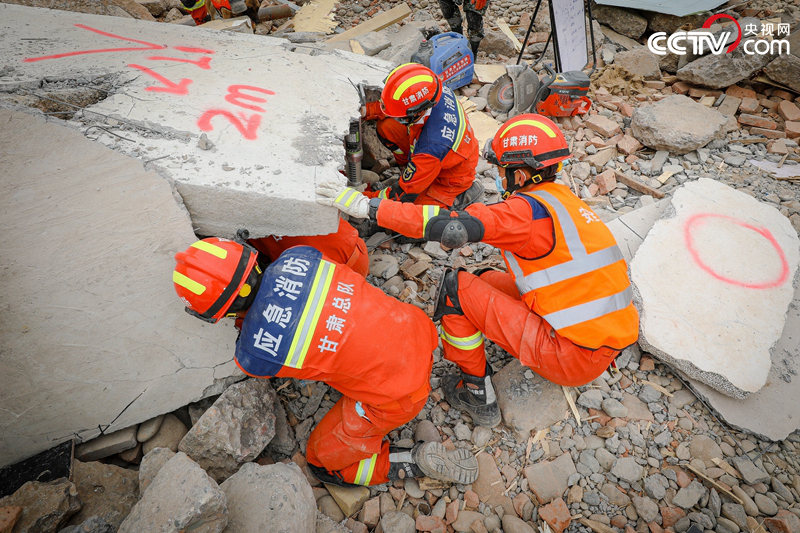

Three firemen are rescuing the trapped people under the marking point.
In this exercise, the fire drill scenarios are all based on the rescue scenarios that may occur due to the earthquake.
During the exercise, fire rescue teams from Gansu, Beijing, Inner Mongolia, Shandong, Sichuan, Yunnan, Xizang, Shaanxi, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang and other places quickly responded to the rally and devoted themselves to the rescue.
Number two: multi-site linkage 1+4+4
The exercise venue adopts the "1+4+4" mode, with the main exercise venue in Zhangye, sub-exercise venues in Jiayuguan, Jiuquan, Jinchang and Wuwei, and four outdoor venues according to scenic spots, high-rise, underground and railways.
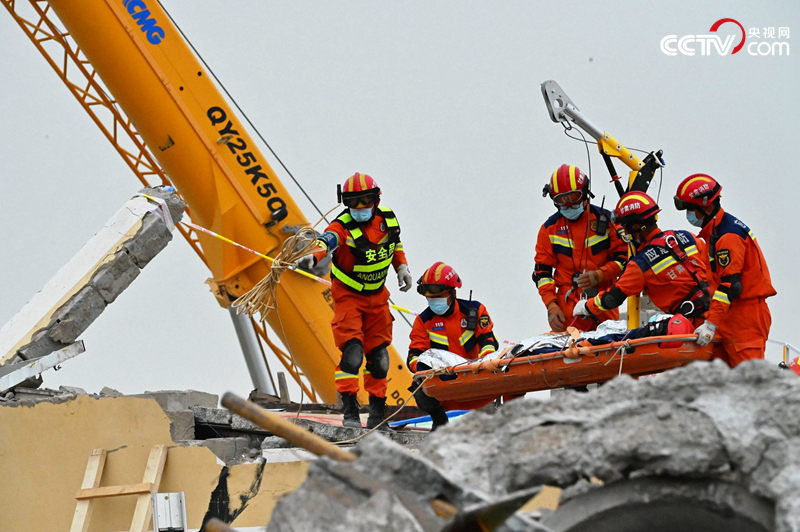

Fire-fighting and rescue workers use construction machinery to remove heavy objects and rescue people trapped in commercial markets.
During the whole drill, in order to cope with the great earthquake and catastrophe in the plateau and cold area, the whole drill was displayed in panoramic mode, which was divided into three stages: pulling inspection, command exercise and comprehensive exercise.
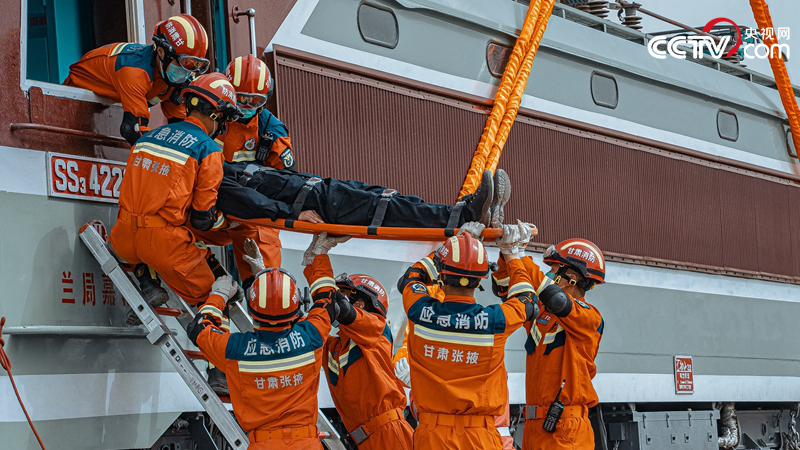

The driver was trapped in the simulated derailment of the Central European train, and the fire rescue personnel carried out rescue.
In this drill, several rescue scenarios that may be caused by earthquakes were simulated, among which Zhangye simulated the search and rescue of people buried in collapsed buildings, the derailment and overturning rescue of trains in Central Europe, the leakage and explosion rescue of oil and gas pipelines for west-to-east gas transmission, the destruction and rescue of facilities for power transmission from west to east, the fire fighting and rescue of high-rise buildings and the construction of camps, the trapped tourists in the Grand Canyon in scenic spots, and the trapped people caused by the collapse of scaffolding in the construction site.
Among them, the west-east gas pipeline leaked and exploded, and huge black mushroom clouds rose one after another. Due to serious deformation and tearing, a large number of crude oil leaked from the Tanlan crude oil pipeline, which in turn caused a fire of 3,200 square meters. The situation was critical, and four professional chemical fire fighting and rescue teams rushed to the scene to reinforce the disposal.
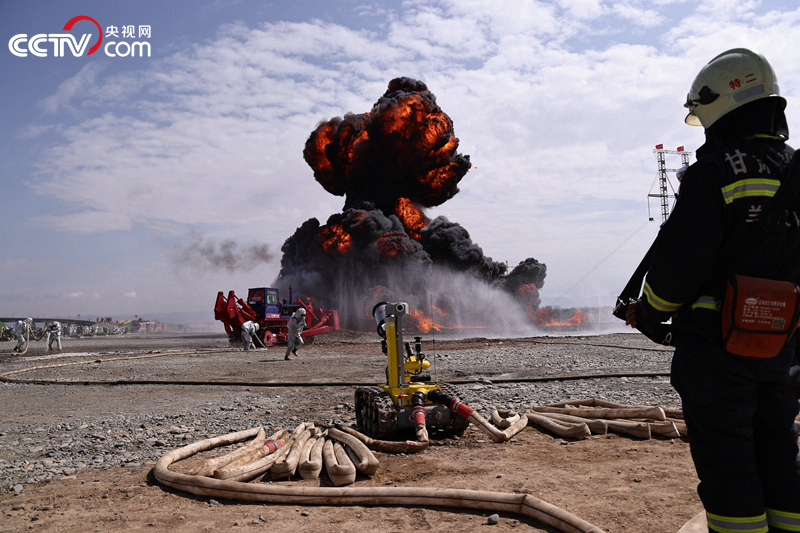

In the oil and gas pipeline leakage, huge black mushroom clouds rose one after another, and fire rescue forces rushed to the scene to reinforce the disposal.
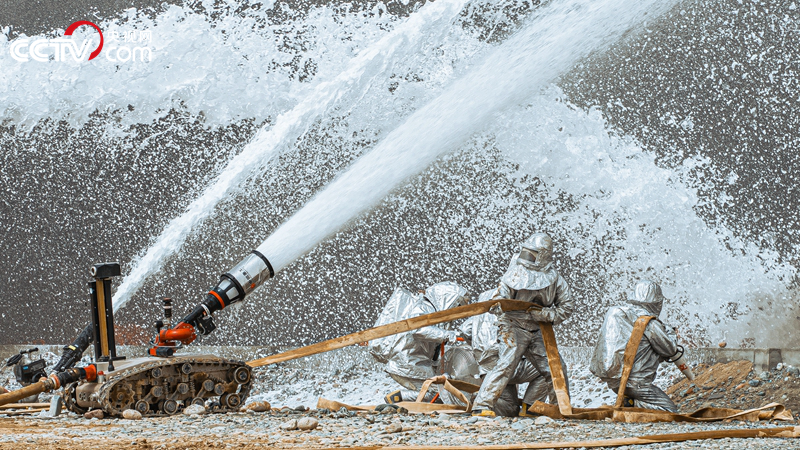

The fire-fighting robot is carrying out the rescue of oil and gas pipeline leakage and explosion.
Wuwei, Gansu Province, simulated the emergency rescue scene affected by the earthquake, where a landslide occurred in Maya Snow Mountain, three climbers were trapped in the snow mountain, and one person showed symptoms of temperature loss.
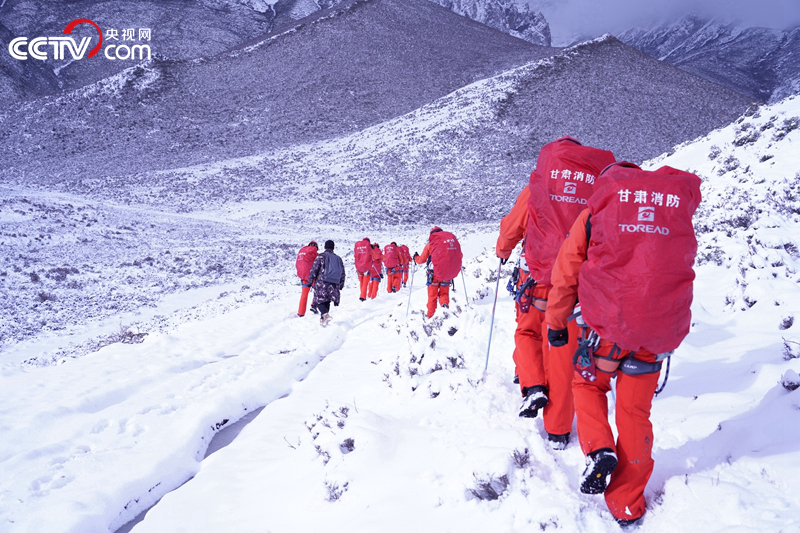

Fire rescue forces wear special equipment for cold prevention and anti-skid to climb 5.8 kilometers of mountain roads and go deep into the snow area to search for missing buried personnel.
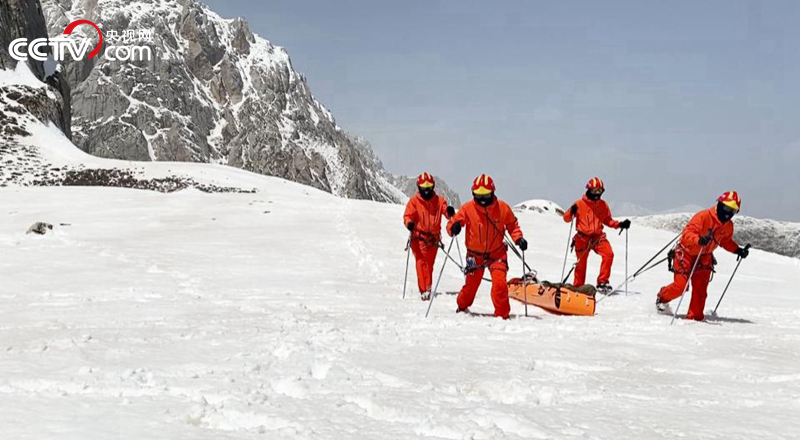

The trapped people are being transferred to the temporary helicopter rescue point.
Jiayuguan City has set up an airport emergency landing course, where the airport runway was seriously damaged due to the earthquake, and the ground broke in many places, so that the aircraft hovering overhead could not land normally. Rescuers are covering the airport runway with a foam layer with a high-magnification foam generator, which can increase the emergency landing buffer, reduce the friction coefficient and reduce the deceleration braking force. Jinchang simulated mine accidents affected by earthquakes.
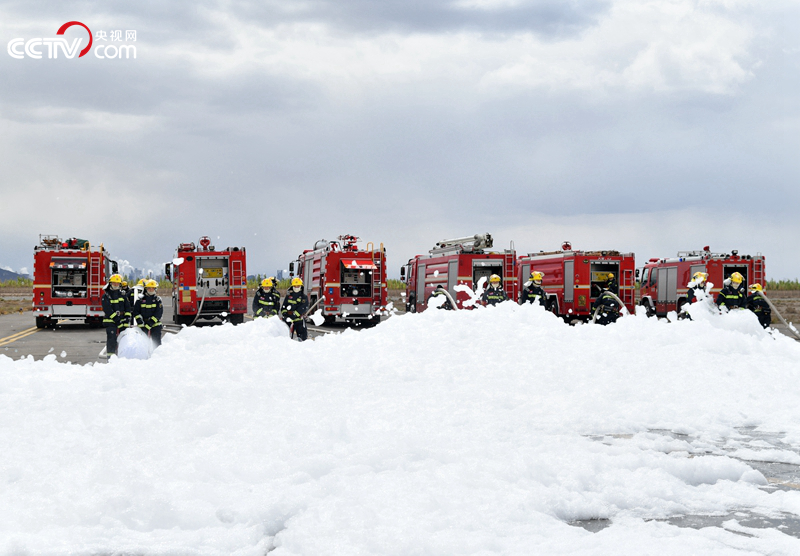

Covering the airport runway with foam layer by using high multiple foam generator.
Houses and oil and gas stations in the living area of refining and chemical plant in Yumen old city of Jiuquan City collapsed and caught fire. Some people were trapped under pressure, some roads were damaged, and power and communication were interrupted.
There are 26 subjects in the exercise, including the rescue of ruins, the capsizing rescue of trains in Central Europe, the leakage rescue of oil and gas pipelines in the West-East gas pipeline, the rescue and transfer of trapped tourists in scenic spots, the fire fighting and rescue of high-rise buildings, the rescue and rescue of people in distress in snowy mountains, etc. The fire rescue team has the courage to take responsibility and overcome difficulties, and participated in a total of 23, which fully reflects the role of the fire rescue team as the "main force" and "national team" of emergency rescue.
From the snowy Maya Snow Mountain, to the vast and colorful Gobi sandbars, and then to the steep Pingshan Lake Grand Canyon, orange figures are everywhere.
Number 3: 2,105 firefighters participated.
A total of 2,105 fire rescue workers participated in the exercise, including 1,533 from Gansu Provincial Fire Rescue Corps and 572 from other teams.
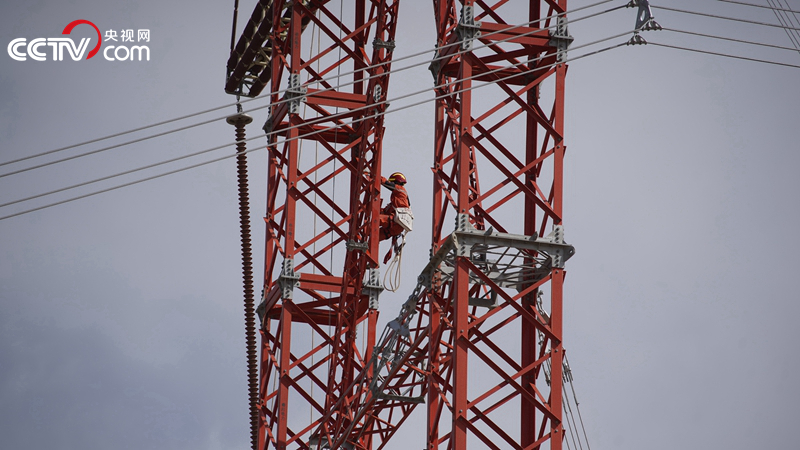

The repair team is repairing the operation.
In addition to specific rescue drill scenarios, it is also crucial to ensure emergency communication through linkage. With the launch of the "Emergency Mission 2022" practical earthquake relief exercise in alpine plateau, extreme situations such as power outage, communication base station damage and public network paralysis have always tested the emergency communication support capability at the disaster site.
After the disaster occurred, the Qiantu Communication Support Team of Zhangye City Fire Rescue Detachment immediately dispatched on-site reconnaissance, established satellite communication links, and reported the disaster at the first time. The emergency communication support detachment of Gansu Provincial Fire and Rescue Corps quickly dispatched to the disaster area to build a command communication network, and mobilized several adjacent detachments to respond synchronously.
Specially modified 10 military three-generation light and high-mobility "Warrior" off-road vehicles are the backbone of emergency rescue and quick dispatch in this exercise, including rescue and obstacle breaking, troop assault, technical rescue, general shelter, communication command, power supply and other vehicles, which are suitable for all-weather, all-terrain and all-regional rescue, and can reach all areas in the province within 10 hours to strive for the "golden rescue period" to the maximum extent.
Number 4: 56,000 pieces of equipment and 70 rescue dogs.
Rescue equipment has also attracted much attention. This exercise carried 56,000 pieces (sets) of advanced fire fighting and rescue equipment in 9 categories, including composite life detectors, high-frequency rescue and cutting sets, large-flow snow cannon robots, large-scale tethered drones, all life-saving robots in waters, heavy-duty support sets, portable electric demolition tools, and mobile lighting lighthouses.
At the scene, the fire reconnaissance robot dog cooperated with modern equipment such as thermal imaging drone to quickly assist rescuers to master the internal situation of collapsed buildings and find the location of trapped people.
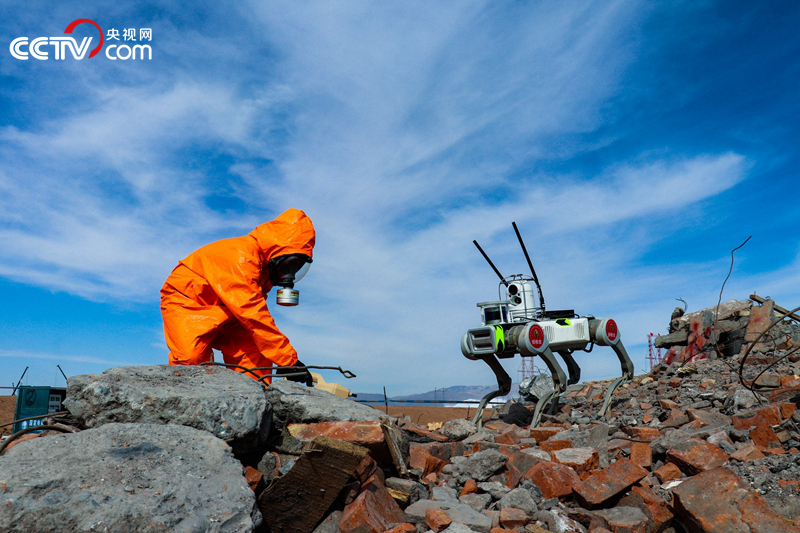

Fire detection robot dog.
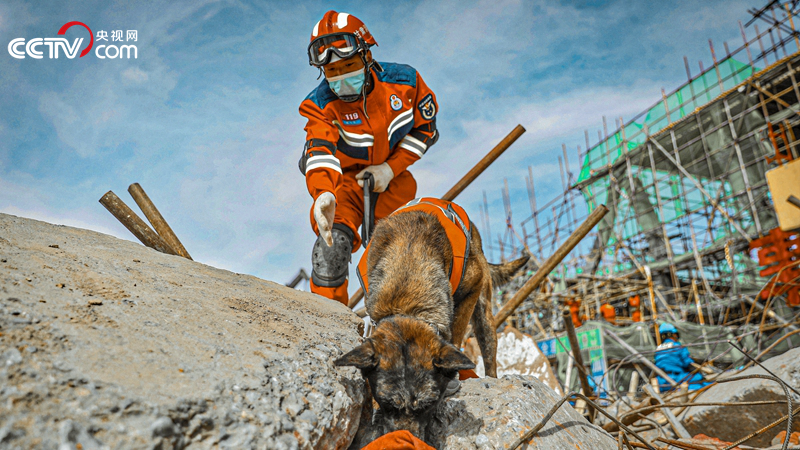

Search and rescue dogs shuttled through the ruins.
The terrain of the ruins is very complex, and the collapsed bodies and scaffolding are staggered and uneven. With the command of the search and rescue dog trainer, six search and rescue dogs quickly shuttled through the ruins, and with the detection of the radar life detector, many shallow trapped people were successfully searched in 20 minutes.
It is reported that the investment in this exercise includes 70 rescue dogs from China’s rescue dog mobile detachments in Shandong and Yunnan and Gansu and Qinghai fire rescue corps. The whole process adheres to the combination of human and dog, dog equipment and search and rescue.